EU VAT Rates Guide for 2025: Standard, Special and Reduced
Did you know that understanding current VAT rates is crucial for navigating the Value Added Tax (VAT) landscape across the European Union in 2025? From the low of 17% in Luxembourg to a staggering 27% in Hungary, the VAT landscape reflects the diverse fiscal strategies of EU member states.
Join us as we explore the intricacies of VAT in 2025, a journey that promises to shed light on this critical component of the EU’s economic framework.
Introduction to VAT Rates
Value Added Tax (VAT) is a consumption tax applied to nearly all goods and services bought and sold for use or consumption in the European Union (EU). The EU has standard rules on VAT, but these rules may be applied differently in each EU country. VAT rates vary across EU countries, with each member state setting its own rates. The standard VAT rate cannot be less than 15%, and one or two reduced rates may be applied to specific goods and services. Understanding VAT rates is crucial for businesses operating in the EU, as it directly impacts their tax obligations and financial management.
What Are the Standard VAT Rates Across the EU in 2025?
| Country | Standard VAT rate | Reduced VAT rate 1 | Reduced VAT rate 2 | Super reduced VAT rate | Parking VAT rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | 20% | 10% | 13% | – | 13% |
| Belgium | 21% | 6% | 12% | – | 12% |
| Bulgaria | 20% | 9% | – | – | – |
| Croatia | 25% | 5% | 13% | – | – |
| Cyprus | 19% | 5% | 9% | – | – |
| Denmark | 25% | – | – | – | – |
| Estonia | 22% | 9% | – | – | – |
| Finland | 24% | 10% | 14% | – | – |
| France | 20% | 5.50% | 10% | 2.10% | – |
| Germany | 19% | 7% | – | – | – |
| Greece | 24% | 6% | 13% | – | – |
| Hungary | 27% | 5% | 18% | – | – |
| Ireland | 23% | 9% | 13.50% | 4.80% | 13.50% |
| Italy | 22% | 10% | 5% | 4% | – |
| Latvia | 21% | 12% | 5% | – | – |
| Lithuania | 21% | 5% | 9% | – | – |
| Luxembourg | 17% | 8% | 14% | 3% | 12% |
| Malta | 18% | 5% | 7% | – | – |
| Netherlands | 21% | 9% | – | – | – |
| Northern Ireland | 20% | 5% | – | – | – |
| Norway | 25% | 15% | 12% | – | – |
| Poland | 23% | 5% | 8% | – | – |
| Portugal | 23% | 6% | 13% | – | 13% |
| Czechia | 21% | 12% | – | – | – |
| Romania | 19% | 5% | 9% | – | – |
| Slovakia | 20% | 10% | – | – | – |
| Slovenia | 22% | 9.50% | 5% | – | – |
| Spain | 21% | 10% | – | 4% | – |
| Sweden | 25% | 6% | 12% | – | – |
| Switzerland | 8.1% | 2.6% | 3.8% | – | – |
| United Kingdom | 20% | 5% | – | – | – |
Introduction
In 2025, the European Union sees a diverse landscape of Standard VAT rates, intricately designed to accommodate the fiscal frameworks of each member state. The Value Added Tax (VAT), a crucial element in the economic structure of EU countries, is applied to most goods and services, directly affecting final consumer prices. This indirect tax system is fundamental to the EU’s internal market, ensuring a harmonized economic environment.
The standard VAT rates in the EU for 2025 vary significantly, ranging from the minimum threshold of 15% to the highest VAT rate of 27% in Hungary, reflecting the autonomy of EU nations in tailoring the tax to their economic needs.
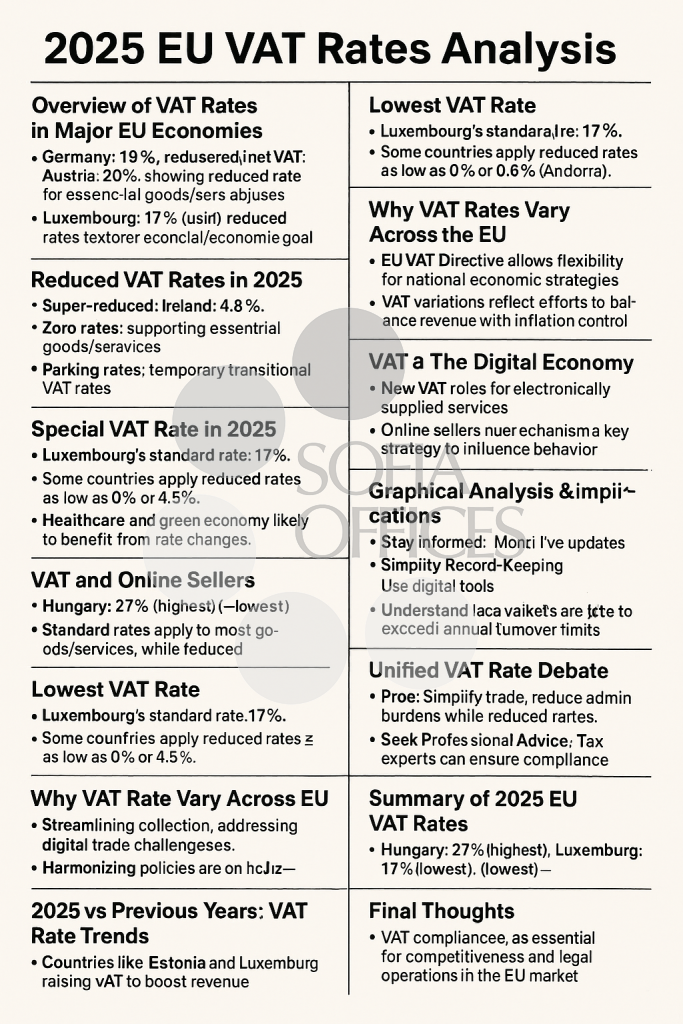
Overview of VAT Rates in Major EU Economies
Germany: 19%, moderate rate.
Austria: 20%, showing close fiscal alignment with Germany.
Hungary: 27%, highest in the EU.
Luxembourg: 17%, lowest standard VAT rate.
Countries like France (super-reduced rate of 2.1%) and Italy use reduced rates to foster economic growth and support specific sectors.
Reduced VAT Rates in 2025
Reduced VAT rates help lower costs for essential goods/services, impacting both consumers and businesses.
- Consumer Savings: Lower costs on food, transport, healthcare.
- Business Growth: Higher demand in VAT-favored sectors like tourism or culture.
- Administrative Considerations: Compliance complexity due to varying VAT rules across countries.
Special VAT Rates in 2025
Super-reduced, zero, and parking rates are permitted under EU law for essential policy goals.
- Super-reduced Rates: E.g., Ireland: 4.8%.
- Zero Rates: Support essential goods/services.
- Parking Rates: Temporary transitional VAT rates.
Case studies:
- Italy: 4% on certain medical goods and food.
- Luxembourg: Super-reduced 3%.
- UK: 20% standard, 5% reduced (post-Brexit example).
Lowest VAT Rate
Luxembourg’s standard rate: 17%.
Some countries apply reduced rates as low as 0% or 4.5% (e.g., Andorra).
Why VAT Rates Vary Across the EU
EU VAT Directive allows flexibility for national economic strategies.
VAT variations reflect efforts to balance revenue with inflation control and social equity.
The Role of VAT in EU Fiscal Policies
VAT is a key revenue tool funding public services and guiding consumption behaviors.
Governments may offer reduced VAT on green goods or essential products to support broader objectives.
Upcoming VAT Adjustments
Minimum VAT remains at 15%; new flexibility to apply two reduced rates ≥ 5%.
Healthcare and green economy likely to benefit from rate changes.
Fossil fuel exemptions to be phased out, impacting carbon-heavy industries.
VAT & The Digital Economy
New VAT rules for electronically supplied services.
Online sellers must comply with VAT in each customer’s country.
Reverse charge mechanism simplifies some digital transactions.
VAT Compliance Tips for 2025
- Stay Informed: Monitor tax updates.
- Simplify Record-Keeping: Use digital tools.
- Understand Local Variations: Research each market.
- Use Technology: Automate calculations and reporting.
- Seek Professional Advice: Tax experts can ensure compliance.
VAT and Online Sellers
Online sellers must charge and remit VAT based on customer location.
EU registration thresholds require businesses to register once they exceed specific annual turnover limits.
2025 vs Previous Years: VAT Rate Trends
Countries like Estonia and Luxembourg raised VAT to boost revenue.
Czech Republic simplified its VAT structure to improve efficiency.
Reclassification of goods/services is a key strategy to influence behavior and simplify tax policy.
Graphical Analysis & Implications
Graphs can show trends and support strategic planning for businesses.
Helps forecast changes and respond proactively to evolving tax policies.
The Future of VAT: Expert Predictions
Streamlining collection, addressing digital trade challenges, and harmonizing policies are on the horizon.
Unified VAT Rate Debate
Pros: Simplifies trade and reduces admin burdens.
Cons: Ignores national fiscal and social priorities.
Ongoing discussion signals potential for deeper integration within the EU.
Summary of 2025 EU VAT Rates
Hungary: 27% (highest), Luxembourg: 17% (lowest).
Standard rates apply to most goods/services, while reduced and super-reduced rates promote social/economic goals.
Keeping up with changes is vital for businesses and consumers alike.
Final Thoughts
VAT compliance is essential for competitiveness and legal operations in the EU market.
Tailored solutions and tax consultation are key to sustainable growth.